In 2024, Traefik v3 officially reached a stable release and brought several important changes with it. One of the more notable updates was the removal of support for InfluxDB v1 metrics.
In an earlier blog post, I shared a guide on how to push Traefik v2 metrics into a Grafana dashboard — but that setup was based on InfluxDB v1. With Traefik v3 now exclusively supporting InfluxDB v2, it’s time to revisit that topic and update the approach.
Let’s dive into how you can adapt your monitoring setup for Traefik v3 and InfluxDB v2.
Introduction
In this blog post, I will provide you with detailed steps on how to activate metrics in Traefik v3 and push them into a containerized InfluxDB v2 database.
Moreover, we will enable logging of HTTP requests for Traefik and use Promtail to push them into Grafana Loki. Finally, we will configure the InfluxDB and Loki data sources in Grafana and import a pre-built monitoring dashboard by me to inspect Traefik metrics and HTTP logs.
The dashboard will look something like this in the end:
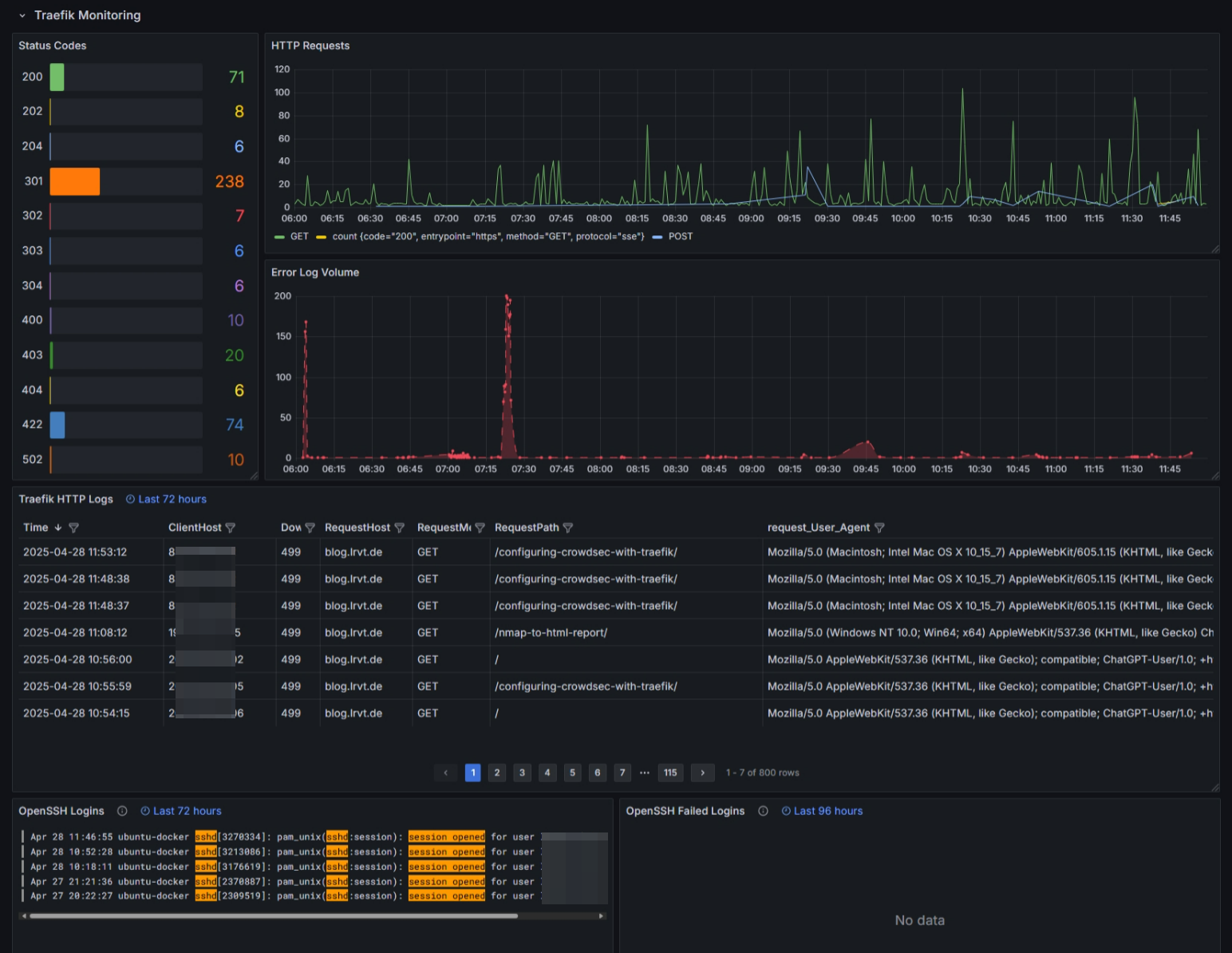
Configuring Container Services
This section contains the mandatory configuration steps for Traefik, InfluxDB as well as Promtail and Grafana Loki.
The general docker-compose.yml file we will be using is the following:
services:
influxdb:
image: influxdb:2.7
container_name: influxdb2
restart: unless-stopped
expose:
- 8086
environment:
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_USERNAME=admin
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_PASSWORD=change-me-1 # <-- change this pw
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ORG=influx-org
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_BUCKET=influx-bucket
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_RETENTION=30d
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ADMIN_TOKEN=change-me-2 # <-- change this pw
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_MODE=setup
volumes:
- /mnt/docker-volumes/influxdb2/data:/var/lib/influxdb2
- /mnt/docker-volumes/influxdb2/conf:/etc/influxdb2
loki:
image: grafana/loki:2.9.11
container_name: loki
user: 1000:1000
command: -config.file=/etc/loki/loki-config.yml
restart: unless-stopped
expose:
- 3100
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:3100:3100"
volumes:
#- /mnt/docker-volumes/loki/data:/tmp/loki # optional data
- /mnt/docker-volumes/loki:/etc/loki # config
promtail:
image: grafana/promtail:latest
container_name: promtail
restart: unless-stopped
command: -config.file=/etc/promtail/promtail-config.yml
expose:
- 9080
depends_on:
- loki
volumes:
- /var/log:/var/log
- /mnt/docker-volumes/promtail:/etc/promtail
- /mnt/docker-volumes/traefik/logs:/var/log/traefik
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana-oss:12.0.0
container_name: grafana
user: 1000:1000
depends_on:
- influxdb2
- loki
- promtail
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL=https://grafana.example.com # <-- adjust
expose:
- 3000
ports:
- 3000:3000
volumes:
- /mnt/docker-volumes/grafana:/var/lib/grafanadocker-compose.yml
As can be seen in the above YML file, we have configured various volume mounts holding our configuration files for the services. In my case, all volume mounts are located at /mnt/docker-volumes/<container-name>. Adjust to your infrastructure setup if needed.
In the following we will discuss the necessary configuration steps for all container services.
Traefik
For this blog post I will not go into detail on how to configure and setup a full-blown, dockerized Traefik v3 instance. If you do not have a Traefik instance yet, may head over to my GitHub repository, which holds all necessary things.
However, in order to push Traefik metrics into an InfluxDB v2 database, you must adjust your static configuration file of Traefik. Add the following code snippet:
metrics:
influxDB2:
address: http://influxdb2:8086
token: change-me-2 # <-- sync with compose env
org: influx-org # <-- sync with compose env
bucket: influx-bucket # <-- sync with compose env
addEntryPointsLabels: true
addRoutersLabels: true
addServicesLabels: true
pushInterval: 60senabling Traefik metrics - traefik.yml
Furthermore, we have to enable access logs for Traefik. To enable access logs for Traefik, adjust your static configuration file again and add the following lines:
accessLog:
filePath: "/logs/traefik.log"
format: json
filters:
statusCodes:
#- "200"
- "400-599"
# collect logs as in-memory buffer before writing into log file
bufferingSize: 0
fields:
headers:
defaultMode: drop # drop all headers per default
names:
User-Agent: keep # log user agent strings enabling Traefik access logs - traefik.yml
That's basically it for configuring the Traefik v3 reverse proxy.
InfluxDB
InfluxDB v2 introduced new environment variables, which support an automatic setup. The configuration file, bucket and organization are automatically created from environment definitions.
Therefore, nothing to manually configure here.
Promtail
In order for our Promtail container to access, read and parse log data, we must specify where our log data is available and which of them should be parsed. The log data must be mounted inside the Promtail container, which we defined in the docker-compose.yml file above.
Specifying which log file to parse is done through a promtail-config.yml configuration file, located at /mnt/docker-volumes/promtail/promtail-config.yml in my case.
For our use case, I'll force Promtail to parse the following two logs:
- Auth logs: We've successfully bind mounted the logs of my Linux server at
/var/loginto the Promtail container. Therefore, let's use it! I want to parse the well-knownauth.loglog file that holds many interersting things such as SSH logins etc. - Traefik logs: Additionally, I want to parse the log files of Traefik. Access logging was enabled previously in the static configuration file of Traefik. The log file will be stored in the directory
/logsof your Traefik container volume.
The configuration file should look like this (nothing to adjust):
server:
http_listen_port: 9080
grpc_listen_port: 0
positions:
filename: /tmp/positions.yaml
clients:
- url: http://loki:3100/loki/api/v1/push
# local machine logs
scrape_configs:
- job_name: auth
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost
labels:
job: authlogs
__path__: /var/log/auth.log
- job_name: traefik
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost
labels:
job: traefiklogs
__path__: /var/log/traefik/*.log
/mnt/docker-volumes/promtail/promtail-config.yml
/var/log/traefik is dependent on the used docker volume mount. In the above defined docker-compose.yml, we mounted our Traefik logs as well as auth logs into the Promtail container.Loki
Finally, we must also define a configuration file for Loki. The file is called loki-config.yml and defined in the above docker-compose.yml. In my case, it is located at /mnt/docker-volumes/loki/loki-config.yml.
The config file should contain the following (nothing to adjust):
auth_enabled: false
analytics:
reporting_enabled: false
server:
http_listen_port: 3100
grpc_listen_port: 9096
compactor:
working_directory: /tmp/loki/compactor
retention_enabled: true
retention_delete_delay: 2h
common:
path_prefix: /tmp/loki
storage:
filesystem:
chunks_directory: /tmp/loki/chunks
rules_directory: /tmp/loki/rules
replication_factor: 1
ring:
instance_addr: 127.0.0.1
kvstore:
store: inmemory
limits_config:
reject_old_samples: true
reject_old_samples_max_age: 168h
retention_period: 360h
max_query_series: 100000
max_query_parallelism: 2
split_queries_by_interval: 0
schema_config:
configs:
- from: 2023-07-01
store: tsdb
object_store: filesystem
schema: v13
index:
prefix: index_
period: 24h
query_range:
parallelise_shardable_queries: false
querier:
max_concurrent: 2048
frontend:
max_outstanding_per_tenant: 4096
compress_responses: true
ruler:
alertmanager_url: http://localhost:9093/mnt/docker-volumes/loki/loki-config.yml
Spawning Our Docker Containers
If you successfully adjusted the above docker-compose.yml file to your needs and ensured that all configuration files for InfluxDB, Promtail and Loki exist, we will now be able to proceed booting up our Docker stack of multiple containers.
A single Linux command from the directory your docker-compose.yml is located and your containers should start to see daylight:
docker compose up -dIf everything went well, you should now be able to log into your Grafana instance at http://<your-servers-ip-address>:3000 via a web browser.
admin.Configuring Grafana
As soon as the Grafana instance is ready, we must complete our last step of adding data sources as well as creating a new dashboard.
Defining Data Sources
Upon logging into your fresh Grafana instance via a web browser, we must specify our data sources.
docker-compose.yml file, the containers will be put inside the same Docker network. Therefore, we can easily use the container names instead of IP addresses.Loki Data Source
Head over to the URL /connections/datasources and chose Loki as data source. Configure it as follows:
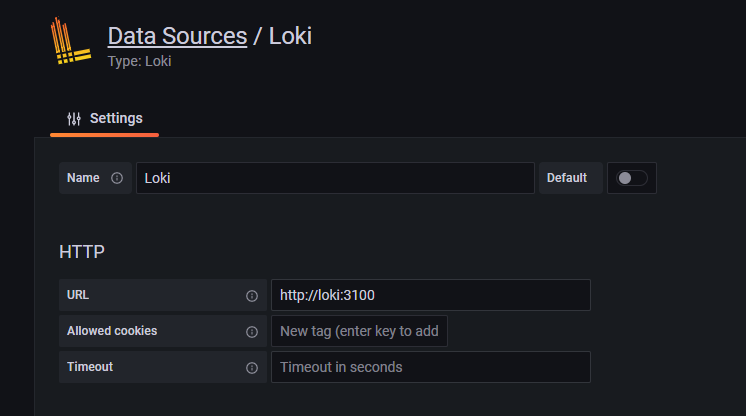
InfluxDB Data Source
Additionally, configure another data source for InfluxDB. Head over to the URL /connections/datasources again and now chose InfluxDB as data source. You must select Flux as query language and define the basic auth login credentials as well as bucket and organization name.
Auth area. The org, bucket and token secret at the bottom at InfluxDB details.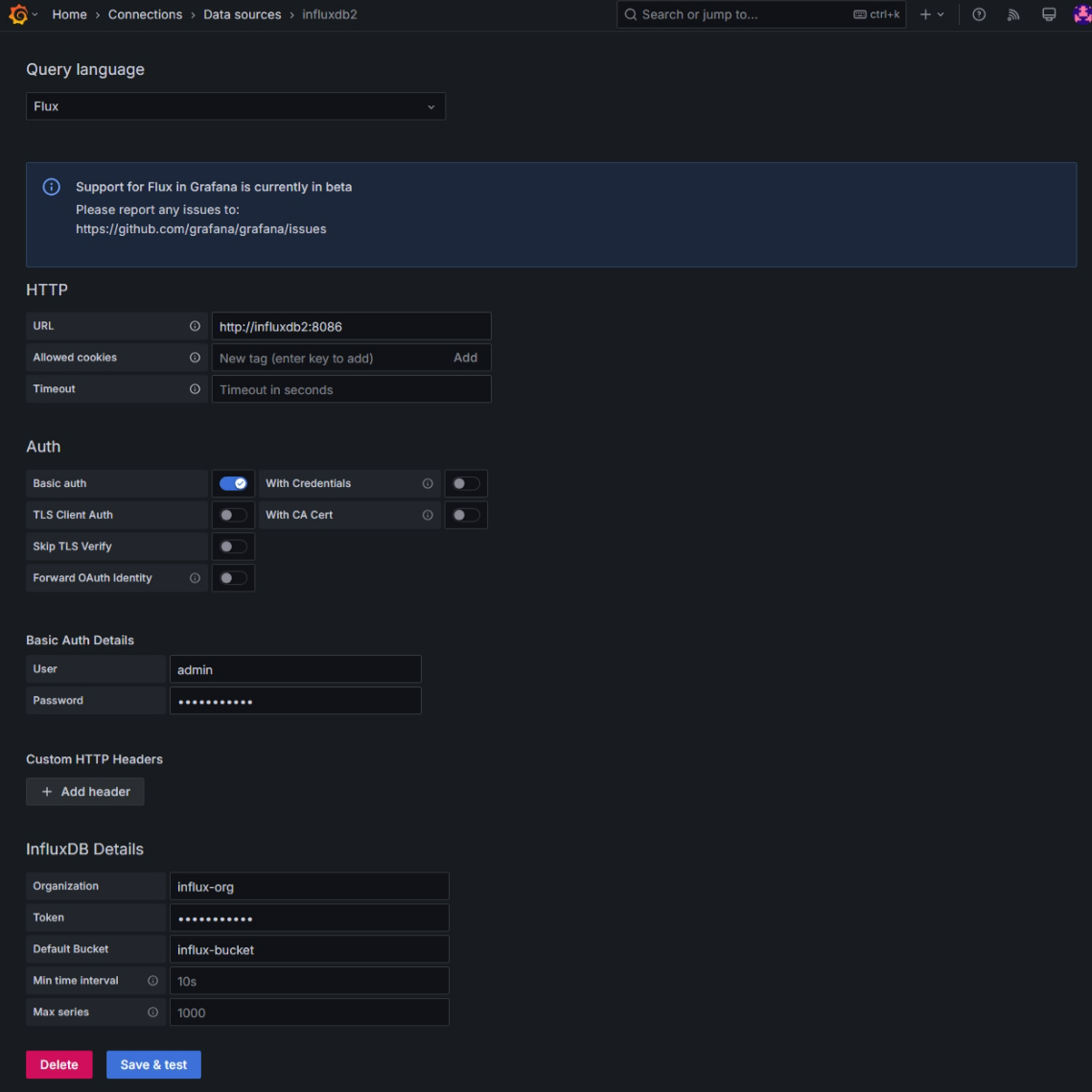
Importing a Dashboard
Finally, we have everything in place to start graphing. Grafana is up and running and we successfully configured InfluxDB and Loki as data sources to pull our data points from. Since creating a Grafana dashboard is kinda time consuming, I have uploaded my template here. Feel free to use it as a starting point:
Browse to the Grafana URL /dashboard/import and upload the above JSON file. Select the configured InfluxDB v2 and Loki sources as default data sources. You should then be redirected to your newly added dashboard automatically, which hopefully displays all statistics correctly.














Discussion